Submit your email address to get a link for quick download on your desktop and get started!
You may need to test serial ports for a variety of reasons. One situation to consider is when you are not receiving an expected data flow. Perhaps you have data acquisition software that should be getting information from a device connected to your computer’s COM port. Unfortunately, there is no data being transmitted and you suspect you may have a communication issue. You want to identify the issue and will need to test the COM port. Now you just need to know how to test serial ports.
Serial Port Tester enables you to test serial ports in Windows 10/8/7 to see exactly what is going on with your serial communication, This enables you to troubleshoot and diagnose communication issues. The first step is to download the RS232 tester software.
Here’s how to check if the RS232 port is working when you have problems with the data flow while using COM Port Tester.
Before you can use the serial port tester you need to provide details about the device you are attaching to your computer.
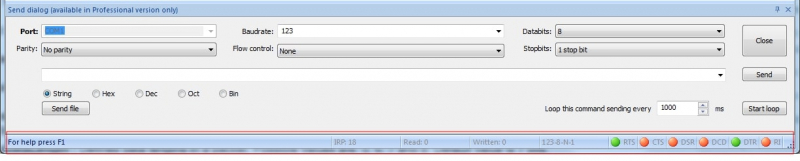
Gather all the device’s details such as the baud rate, the number of serial ports to which it is connected, data bits, and parity. You can use a value of 2 for the top bits if you don’t know how many are in use. This will not cause any harm except to possibly slightly slow down data transmission. You can query and monitor the status of current connections to your machine with Serial Port Tester’s COM Port Status window.
Note: Detailed information concerning each setting can be obtained by reviewing the device’s documentation.
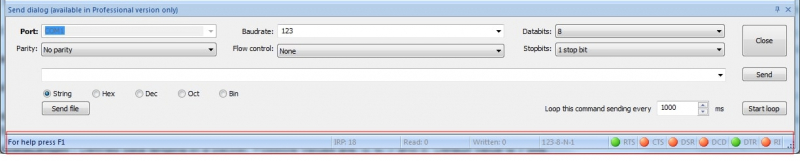
Serial port control information is displayed as a collection of 4 or 5 items, each separated by a dash. In the fling list, a leading “n” indicates a numeric item and a “c” designates a character item.
Defines the serial port baud rate or transmission speed. Possible values are: 110, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 38400, 56000, 57600, 115200, 128000 and 256000. If no value is set, a default of 110 is used.
Parity can be defined with one of these values: (E)ven, (O)dd, (M)ark, (S)pace, or (N)one. (N)one is the default.
Defines the flow control used in the connection. It can be set to Hardware (P), Xon/Xoff (X) and None. The default setting is None.
Defines the length of a data packet. Possible values are 5, 6, 7 and 8. The default is 7 bits.
Defines the number of stop bits. Possible values are: “1”, “1,5” and “2”. Default value is “1”.
Using a quality software tool can help you identify and address issues quickly. Electronic Team’s Serial Port Tester offers an excellent solution that provides users with an advanced feature set for diagnosing serial communication problems. Its versatility and flexibility make this a valuable addition to the software tools available to individuals working with serial applications and devices.
Follow these steps to initiate a new testing session after you have defined the settings for the connection.
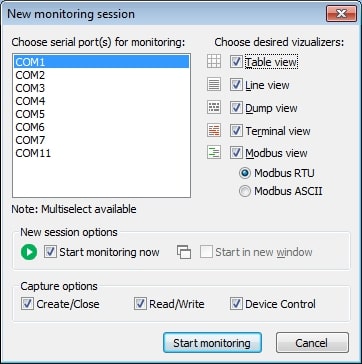
You can control how a new monitoring session begins with the “Start monitoring now” and “Start in new window” checkboxes.
Select the capture options from these choices: Create/Close, Read/Write, and Device Control.
Click the “Start monitoring” button to start the new session after all the options have been set.
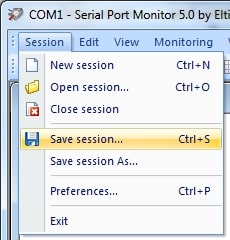
Specify a file name at the prompt so you can reload the session later to work with it further.
DTE equipment may require you to use a null-modem adapter to conduct a serial port test. Rewiring the cable connector is another option that more technically proficient users might attempt.
Note: At times it can be difficult to identify the type of device in question. The documentation is often sketchy and you may need to use your deductive powers by looking at the device’s other signals. Devices such as modems have a DSR as an output and use the DTR as a counter.
Other manufacturers reverse this labeling, making it challenging to figure out the device’s signals.
With correctly named signals you end up with:
The crossed connections described define a null-modem configuration. When deciding how to test a serial port, you may need to purchase an adapter to implement this connection.
You are ready to test RS232 ports once you have the signal wires connected correctly. If you are still not successful in receiving data, you might need to investigate the handshaking lines in order to test serial ports.
Handshaking does not need to be implemented just because a device has the capability to do so. In many cases, manufacturers put the signals on the plug as they are easily available from the unit’s processor. If you choose to use handshaking, it is advisable to start with lines carrying fixed voltages. This minimizes any effects on the equipment’s operation. In cases where resistors are tied to handshake lines, you do not need to connect them.
If you choose to implement handshaking with your RS232 tester, you should know that Serial Port Tester supports DTR / CTS handshaking. Using the tool, the computer employs its DTR output to indicate it is available to receive data. Devices can take advantage of the CTS input to limit the data flow from the computer.
The only time that the computer’s CTS input is important is when you are performing hardware handshaking. If you are not using hardware handshaking the CTS is ignored, but a high level is maintained on the DTR so you can use it to tie unused inputs to the device.
This change should be performed on the device’s end of the cable. After making the modification, ensure that data is still flowing through the cable.
A software protocol that enables Xon \ Xoff handshaking can also be used to control the flow of data between a computer and a connected device.
The protocol works by a device sending an Xoff character when it cannot receive any more data. Transmission is halted until an Xon character is sent and received by the computer which informs it to restart the communication. Xon and Xoff characters can be sent by the device or computer.
Software handshaking is supported by COM Port Tester if it is required by the device you are using.
Once serial communication issues have been solved by the previously outlined steps, you can return to step one and check the status of your serial port lines.
Below the main table, the states of the serial control lines are displayed.
The RS232 port test is facilitated by a graphical display of the status of the lines. A green circle indicates a high level with red representing a low level and gray pointing to a line with an undetermined state.
It can be hard to pinpoint the cause of serial communication problems. Some of the more common methods of diagnosing the issue have been discussed in the article.
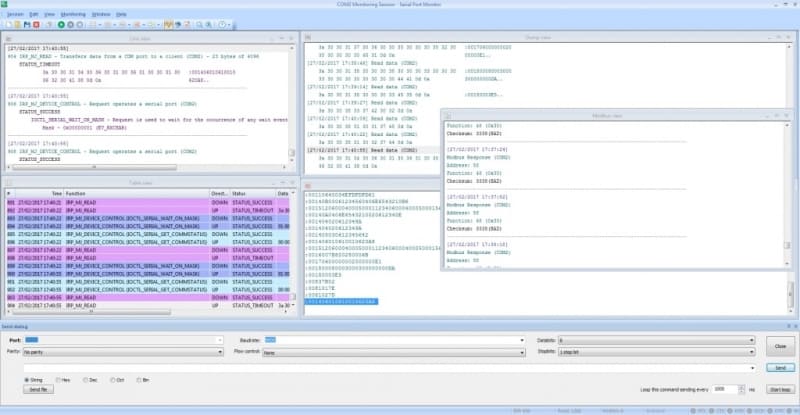
In conclusion, testing serial ports can be essential when troubleshooting communication issues between your computer and connected devices. By using Serial Tester Software, you gain visibility into the details of your serial communication and can methodically identify and resolve problems. Key steps in the testing process include setting up serial port details, understanding and adjusting baud rates, data lengths, and handshaking options, and using specific diagnostic modes within the tester software, such as Dump view or Modbus view, for real-time feedback on the data flow.
In some cases, additional configurations like null-modem adapters or fine-tuning handshaking lines may be necessary to establish or maintain proper communication. Whether using hardware or software handshaking, these settings can prevent data loss and improve the reliability of the serial connection. With a clear understanding of these tools and techniques, users can efficiently test, diagnose, and ultimately improve their serial port communication setups, ensuring smooth data transfer and system functionality.