Serial Port Logger is a Free COM port software to record all serial communication data into a text file. It easily collects data from a serial port device and saves this precious information into a new text file or continues from previous session.
This Free Serial Data Logger licensed as Open Source Software.
Contents
RS232 Data Logger Usage
Using Serial Data Logger software enables you to analyze serial transmission which can be helpful in a number of situations. You can use the information to obtain a better understanding of serial ports and traffic. You can employ a COM port logger to collect data from a GPS unit to track movement or simply to conduct further analysis on serial activity.
Log serial COM port and track serial dataflow changes
RS232 Logger has a simple interface, so to begin serial logging you just need to select the serial port, choose where to file serial communication data, define RS232 port's parameters and click "Start". Logs in the text file will represent all details about serial port communications and RS232 dataflow.
Test RS232 communication between serial port devices and applications
FREE Serial Port Logger can be installed and used under Virtual Machines, like VMWare or Virtual PC. Such functionality can be successfully used for testing. Our Serial Port Logger is great for learning purposes, too.
Serial Data Logger Guide
After you download, install, and launch the RS232 Data Logger, you will be presented with its intuitive user interface. Logging serial traffic is easily accomplished by choosing the serial port to log and a file which will hold the redirected data. Then, specify the parameters of the serial port and click the “Start logging” button.
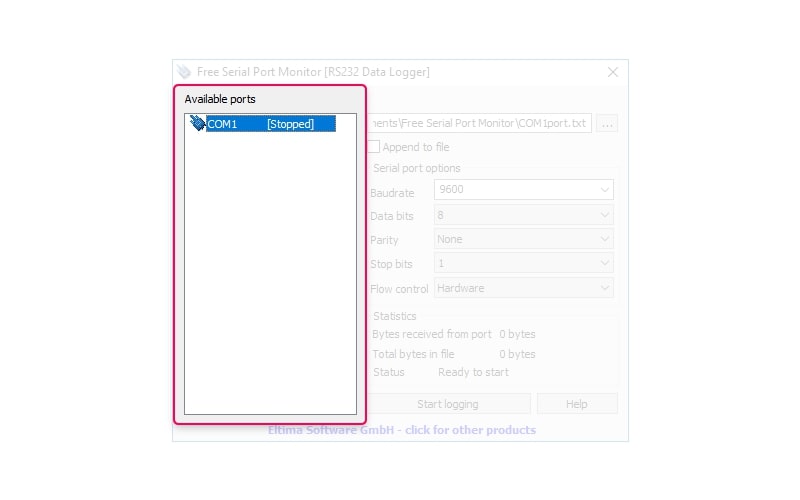
Available ports
This panel displays the serial ports that are available on your system and their logging status. Virtual and real serial ports are handled identically by the RS232 Data Logger.
Log file
The “Open file” button launches a dialog box where you choose the destination file to be used for logging. The file name is displayed in the “Log file” text box. Simply selecting a file name does not initiate logging. This must be done by clicking the “Start logging” button.
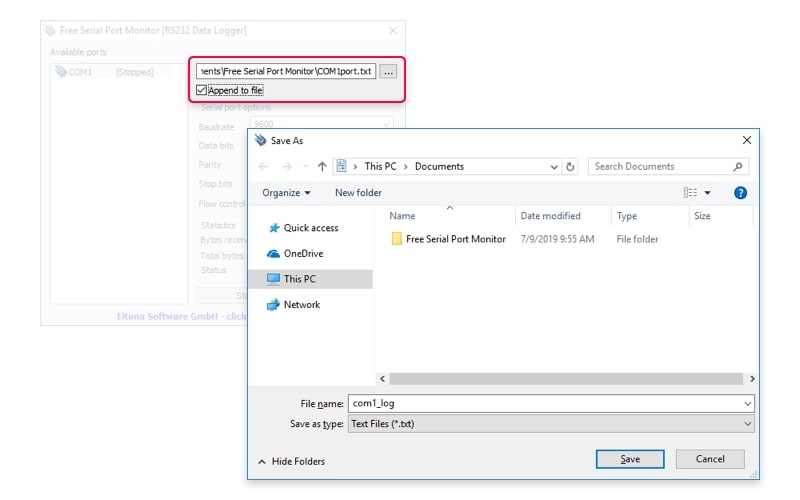
Append to file
This option determines if the data captured by the RS232 logger is appended to the end of an existing file. The alternative is to clear the file and start logging to an empty file.
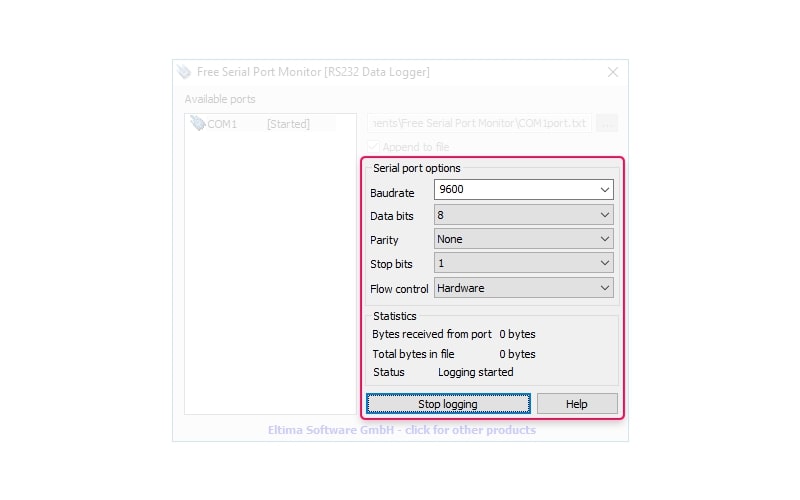
Serial port options
Select the parameters of the serial port you need to log. These parameters must match the values of the port in question or the attempt to log the data will fail.
- Baudrate specifies the serial port’s transmission speed in bits per second. For example, “1200 baud” indicates that the port’s top speed is 1200 bits per second. RS232 Data Logger supports all standard baud rates from 100 up to 256000 bits per second.
- Data bits option indicates the number of data bits the port will transmit. Serial communication involves sending data bits as well as a start and stop bit and a parity bit if parity is being checked. The data bits contain the transmission’s useful information. The data bits parameters can be set to five, six, seven or eight with the least significant bit sent first. Sending ASCII characters demands at least seven data bits, while binary data requires eight bits to transmit. Certain specialized communication equipment makes use of the five and six data bit formats.
- Parity determines if parity will be checked. There are five options from which to choose. They are none, odd, even, mark or space. When set to none, no parity bit is sent and checking is not implemented. When employing even parity, the data’s mark bits are counted and the parity bit is set or cleared to end up with an even number of mark bits. Odd parity is similar but the parity bit is set if needed to obtain an odd count of mark bits. Mark parity always sets the parity bit whereas a parity of space indicates the parity bit is unasserted.
- Stop bits option defines how the end of a byte is designated. It can have a value of 1, 1.5, or 2. The majority of modern devices are designed to use 1 Stop bit.
- Flow control indicates the type of Flow control that will be used. This parameter ensures that the device receiving the serial data can handle the transmission. The RS232 data logger software lets you choose between Hardware, None or Xon/Xoff which are used for asynchronous communication.
Statistics
Real-time data is presented by the RS232 Data Logger through the use of two distinct counters. The total number of bytes received from the port and logged to the files are shown in the “Bytes received from port” and “Total bytes in file” fields in the statistics section of the interface. The status of the serial port is also displayed. These statistics are used to ensure that the communication data is being correctly logged.
Start logging
This button is used to initiate the logging procedure with the port and parameters you have selected. When logging is occurring, the button changes to a “Stop logging” selection used to terminate the logging session.
Help
The software’s user manual is accessed through this selection.