Submit your email address to get a link for quick download on your desktop and get started!
Professional audiovisual (A/V) equipment is often controlled through the RS-232 serial communication protocol, a long-standing standard for linking and managing devices. RS-232 enables communication between various devices, including amplifiers, switchers, dimmers, extenders, and projectors, making it invaluable in complex signal management systems.
Despite its widespread use, RS-232 connections are not immune to issues, and troubleshooting them can save significant time and frustration. Here’s a guide to understanding common RS-232 serial port problems and effective solutions.

Contents
RS-232 communication, while robust, can suffer from a range of issues, from mismatched settings to physical connection problems. Below are the top five common issues you might encounter, along with solutions to get your system back on track.
One of the most frequent culprits behind RS-232 connection failures is mismatched communication parameters. For two devices to communicate correctly, they must share identical settings, including:
If these parameters don’t match between your control device and the controlled equipment, communication won’t work. Ensure both devices have identical settings to establish a stable connection.
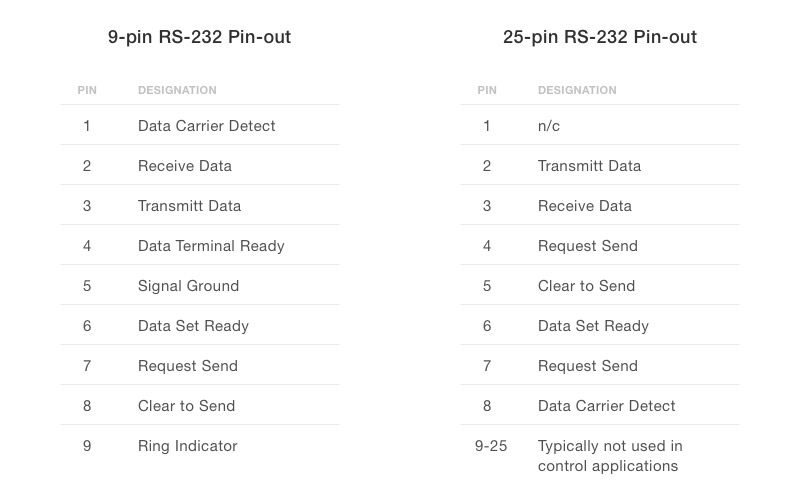
Using the wrong type of serial cable can easily lead to connection issues. Serial ports typically connect through 9-pin or 25-pin connectors, and the cable must match the port type on both devices. Additionally, RS-232 applications generally require either a “null-modem” or “straight-through” cable, each suited for different types of communication:
To avoid connectivity issues, ensure you’re using the correct cable type for your specific application.
Faulty or improperly connected cables are another frequent cause of RS-232 issues. A simple fix is to check the cable for any loose connections and ensure it is firmly plugged into both ports. If problems persist, consider replacing the cable entirely, as physical wear and tear can impair the data transmission quality over time.
Software drivers are essential for communication with RS-232 devices. If a driver is improperly installed or incompatible with the system, the serial port may not function correctly. Re-installing the driver or updating it to a compatible version can often resolve these issues. Additionally, check that your serial port settings within the software align with those of the connected device to eliminate any potential conflicts.
For control systems to function with RS-232, correct wiring is crucial. Most setups require a connection between the transmit (TX) and ground (GND) pins on the control system to the receive (RX) and ground (GND) pins on the controlled device. If a response is needed, an additional wire may be required. Reversing these connections can disrupt communication, so verify wiring before proceeding with software checks.

One of the most common serial port errors that installers encounter when connecting a device to the control system is incorrect wiring. Most control systems only require the connection of two wires to the controlled device. The Transmit (XMT) and Ground (GND) pins on the control system are connected to the Receive (RCV) and Ground (GND) pins on the controlled device respectively, as shown below (Fig. 1).

If the control system needs to receive a response from the controlled device, a third wire will also need to be connected (Fig. 2). For example, this is the recommended wiring if you are controlling a device through your computer’s COM port.

If all of the pins are not labelled it can be difficult to tell if the wiring between control system port and controlled device port has been done correctly. If a terminal block connector is in use you can use a voltmeter to monitor the voltage and ascertain that the connection is good. Test the voltage with the voltmeter set to “DC”. You want the reading between the RCV pin and the GND pin on the terminal block connector to be between -12V and -6V. Your XMT line should have the same reading as seen below (Fig. 3)

If the voltage on the receive line remains at 0 volts after you have connected the control system and the controlled device, this indicates that your serial port connection problems are the result of the Transmit and Receive lines being reversed (Fig. 4).

Once the hardware connections are verified, check the software settings. Communication parameters like baud rate, data bits, parity, and stop bits must match on both devices. The typical settings for A/V devices are 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit, also known as “8N1.”
A serial port debugging tool can significantly simplify troubleshooting.
Serial Port Debugger by Electronic Team, for example, allows users to monitor and log serial port activity, helping them analyze data in real-time. It also enables emulation and playback of data transmissions, allowing users to identify discrepancies across multiple instances and pinpoint potential issues.
RS232 debug software can prove to be an indispensable tool when confronted with serial port communication problems. Put it in your software toolbox today and start streamlining your troubleshooting sessions
The RS-232 protocol has been an industry standard since the 1960s, adapted over the years to ensure compatibility with various international standards. This protocol generally uses either 9-pin or 25-pin connectors, with the more compact 9-pin configuration commonly found in A/V equipment.
RS-232 operates within a voltage range of -15V to +15V, providing a high tolerance for interference and signal degradation. However, this wide voltage swing can generate significant electrical noise, so it’s advisable to keep RS-232 cables away from audio or microphone lines to avoid crosstalk and signal interference. Proper shielding of nearby audio lines can mitigate noise issues if close proximity is unavoidable.
Cable length directly impacts baud rate performance in RS-232. For baud rates at 1200 to 2400, cable lengths of up to 100 feet are generally acceptable. At higher baud rates (e.g., 9600 and 19200), cable lengths should be reduced to 50 feet or even 20 feet to maintain a stable connection. Choosing the correct cable length for your baud rate will improve signal integrity and minimize data loss.
Troubleshooting RS-232 connections can be straightforward when you understand common issues and take a systematic approach. From ensuring correct communication settings and cable types to verifying wiring and using serial port debugging tools, these steps can save both time and frustration. Whether you’re managing a professional A/V setup or a control system, mastering RS-232 troubleshooting can help you maintain reliable, effective communication across your devices.